Events
Overview
This guide covers an important concept in Noodl called Events. Events are used to send and recive signals with accompanying data. Signals are sent from one part of the node graph to one or many other locations in the graph. This is often useful when a user interaction occurs in one place of the app, such as the click of a button, that should trigger an action in a different place, e.g. a popup showing.
What you will learn in this guide
This guide will teach you how to use the Send Event and Receive Event nodes to pass signals and data from one place in your node graph to another.
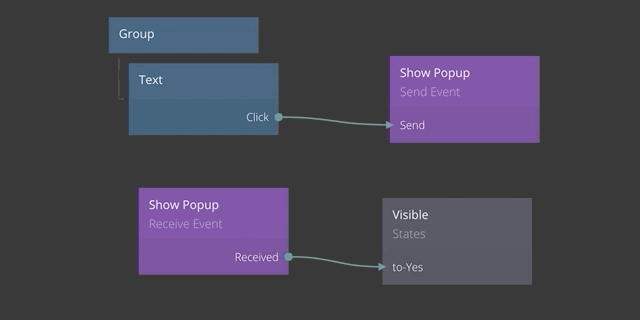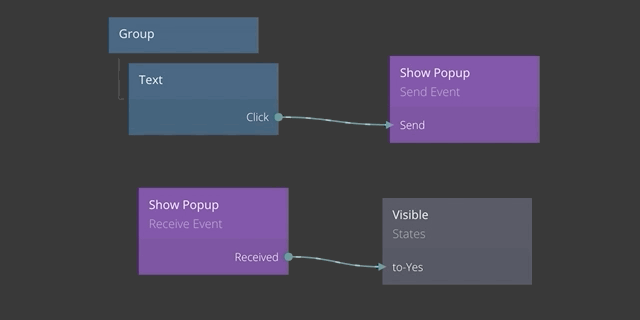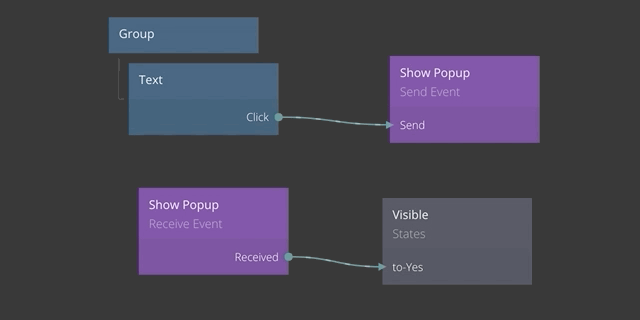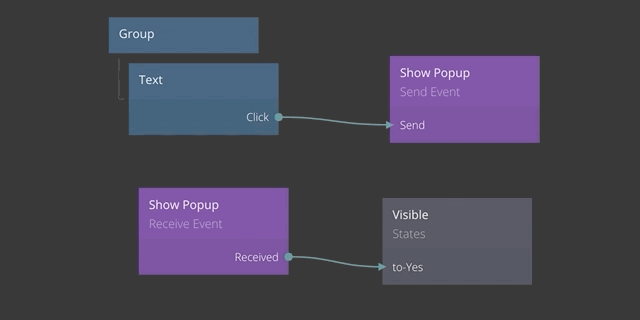
This concept includes two nodes, the Send Event node and the Receive Event node. As the name implies, the Send Event node is used when you want to send an event. Below is an example of an event being sent when a Text node is clicked.
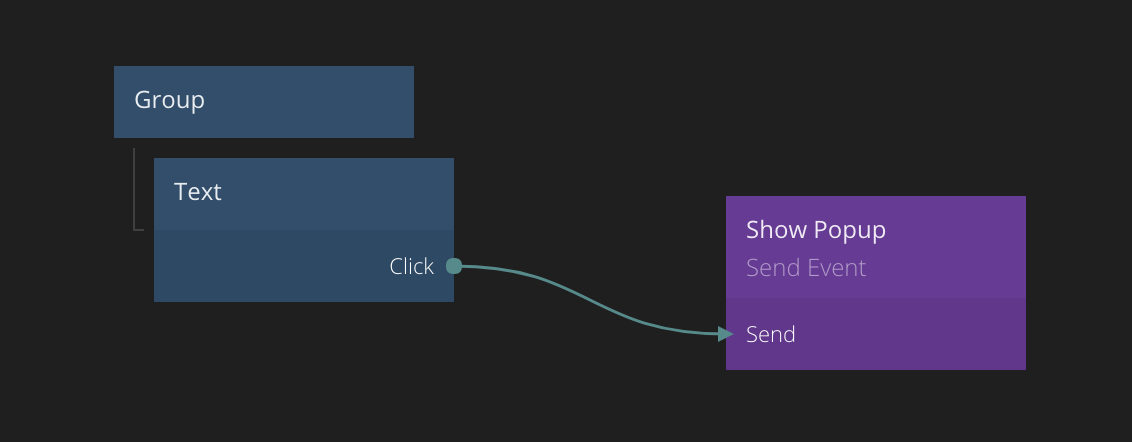
Sending and receiving events
In the example above, the Click signal of the Text node is connected to the Send input of the Send Event node. This will trigger the an event to be sent when the text is clicked.
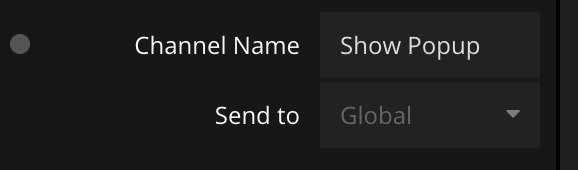
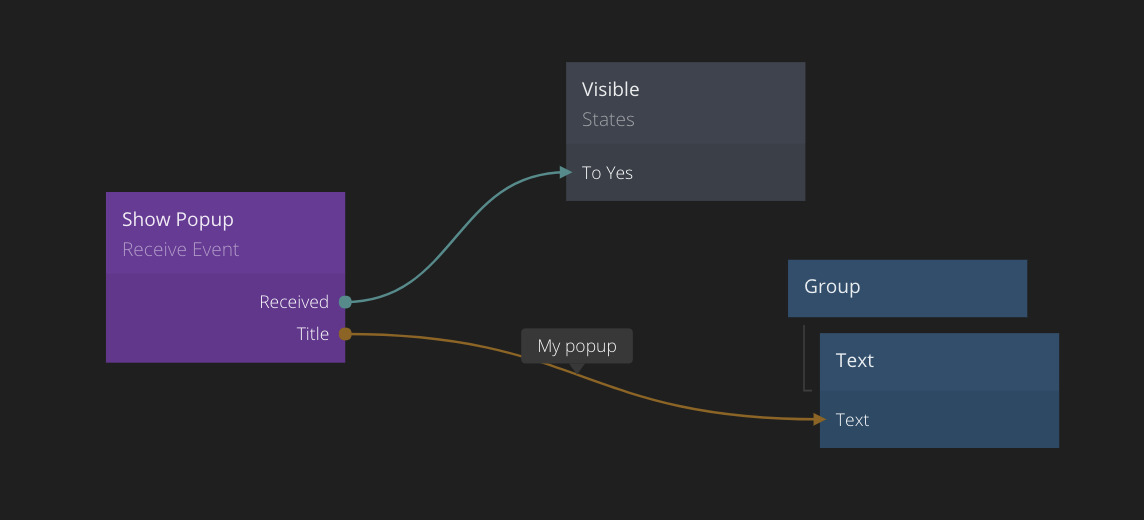
An event is sent to a certain Channel which is specified in the properties of the Send Event node. In this case the name of the channel is Show Popup.
The event signal is passed to all Receive Event nodes that share the same Channel. In the example below the event that was sent above is received.
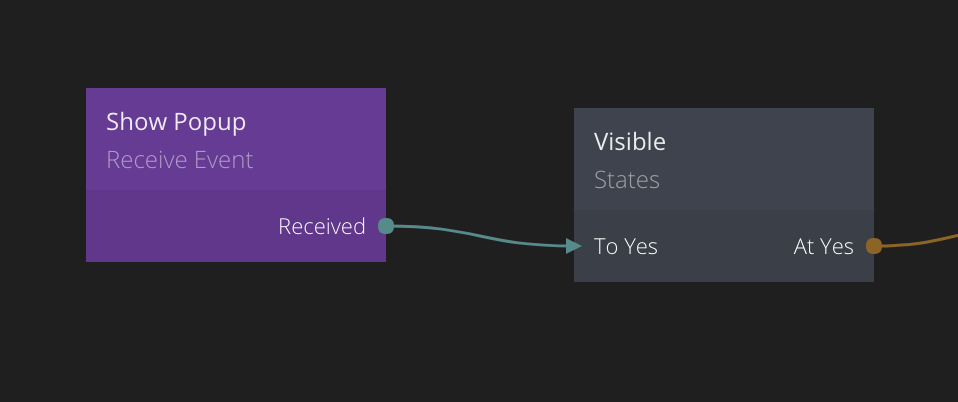
To illustrate this you can see below how when the click signal is sent via the Send Event node, it is passed to the Received output of the Event Receiver node.
Passing payload data
So far we have seen the basic concept of the events mechanism in Noodl. Next, let's take a look at how you can pass data via payload connections to your event nodes. You start by adding ports to the Send Event node. You can add any number of ports for the data that you want to pass with the event.
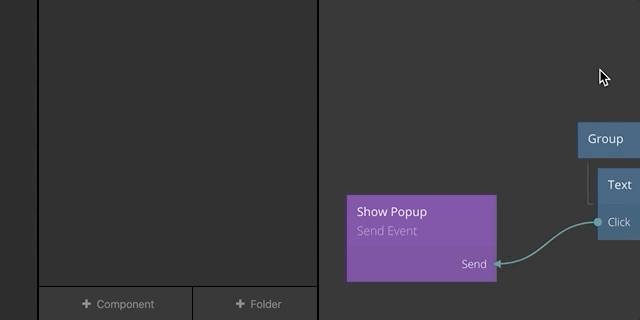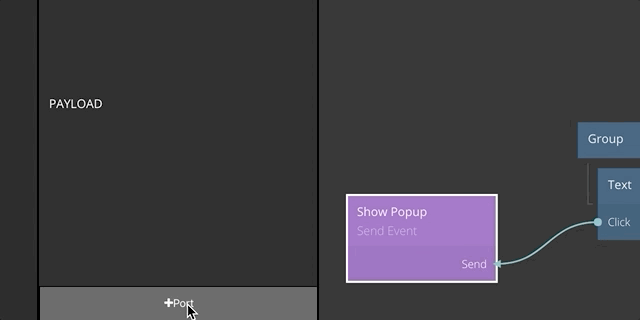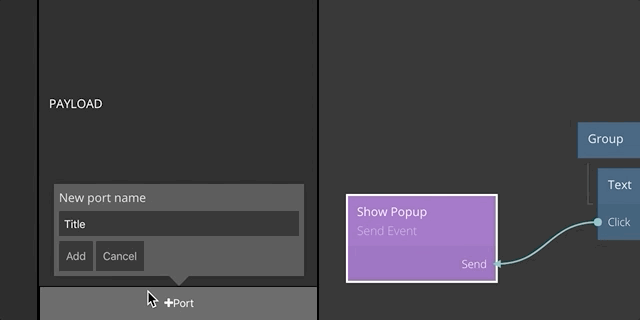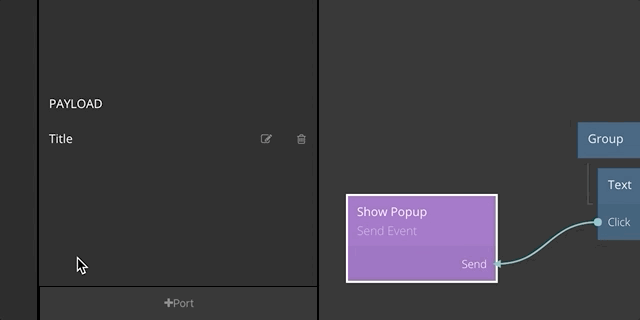
Now you can connect data to the input ports that you created on the Send Event node. When the Send signal is received, the values on all inputs of the Send Event node will be captured and passed to the Receive Event.
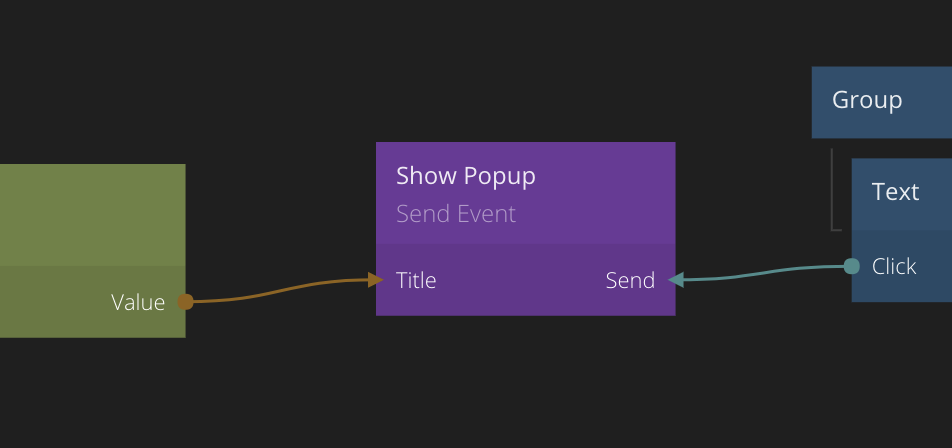
When the Receive Event node outputs the Received signal it will also update all other outputs. The payload ports added on the Send Event node will become available on all Receive Event nodes that share the same channel as the Send Event node.
Propagation
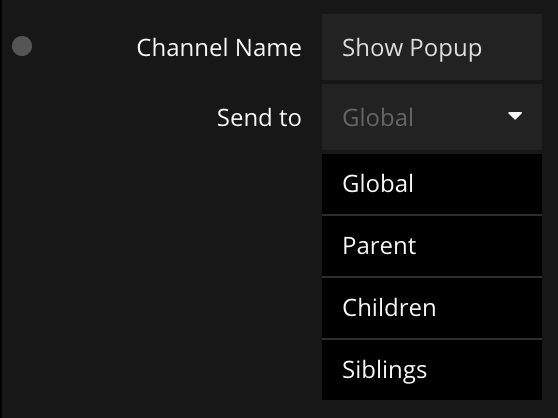
Event propagation means how an event is sent in the graph, i.e. which Receive Event nodes an event is sent to. The default propagation mode is Global which means all receivers will be triggered. You can however change the propagation via the Send To property of the Send Event node.
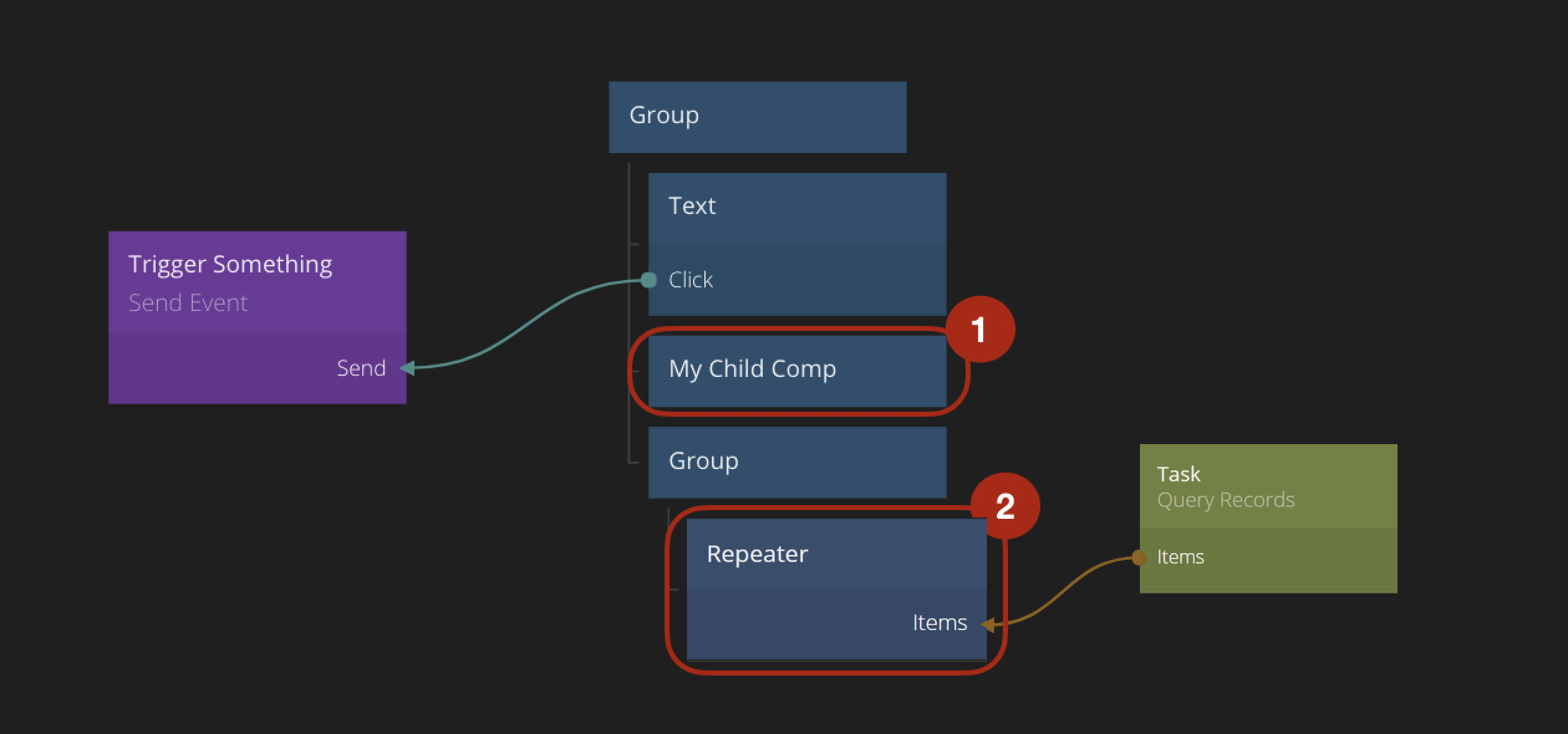
The Children mode will send the events to all the children in the component where the Send Event node is. So in the example below, the event will first be sent to My Child Comp followed by any children that node may have. When all descendants of My Child Comp node have received the event it will pass it to all children that are dynamically created by the Repeater node, and their descendants.
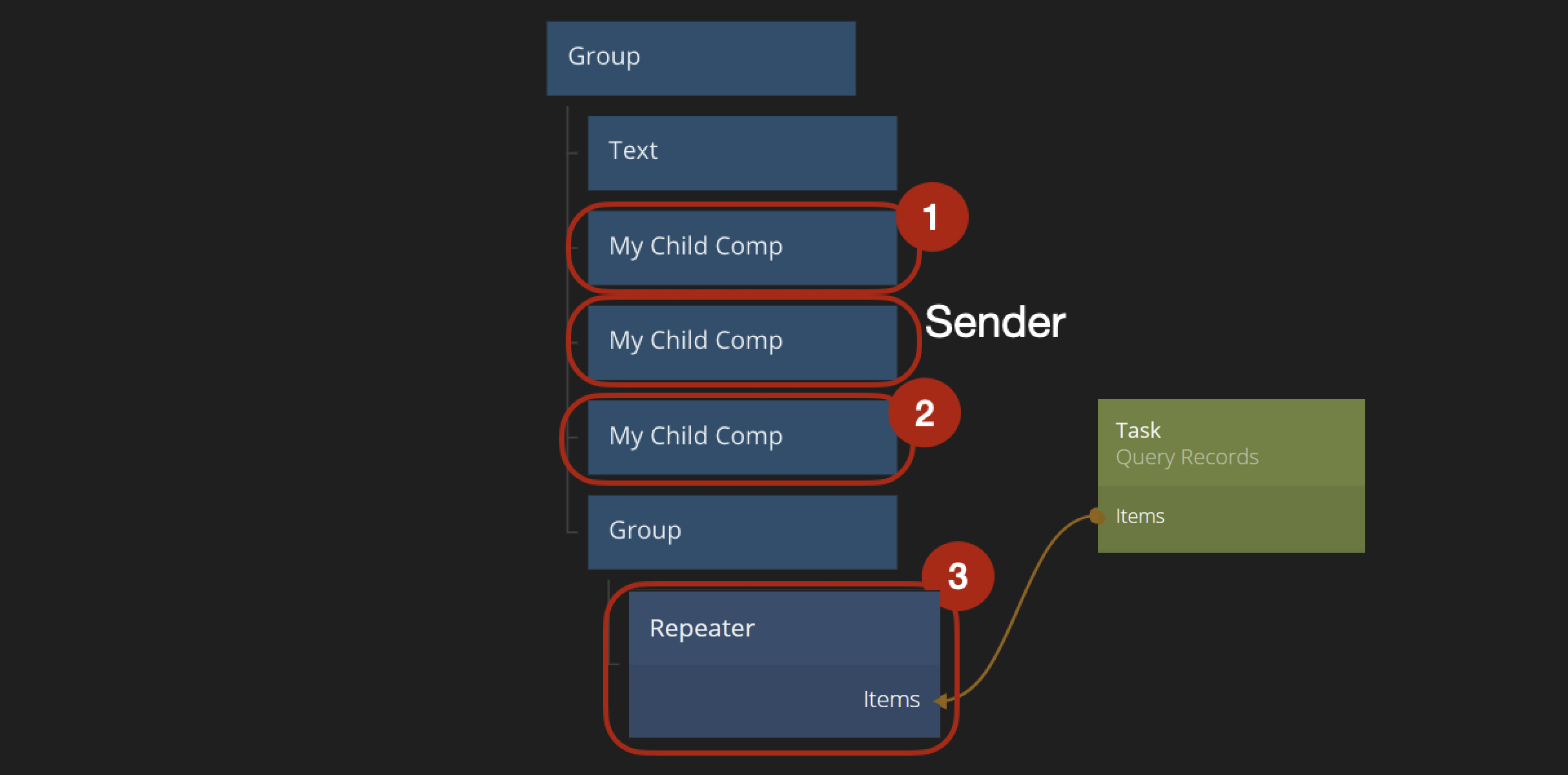
The Siblings mode will pass the event to all other nodes that are on the same level as the node where the originating Send Event node is. So if for instance the My Child Comp in the graph below contains a Send Event node that sends an event to its siblings all other My Child Comp nodes will receive it, except for the one sending the event, followed by the child instances dynamically created by the Repeater node.
The last propagation mode is Parent. This mode will send events up the node graph hierarchy. The My Other Child in the example graph below contains a Send Event node that is using the Parent propagation mode. When an event is sent from My Other Child, the parent My Child Comp node with receive it, followed by the node we are in and then the event would be passed on to the parent of this node. The propagation follows the visual hierarchy chain.
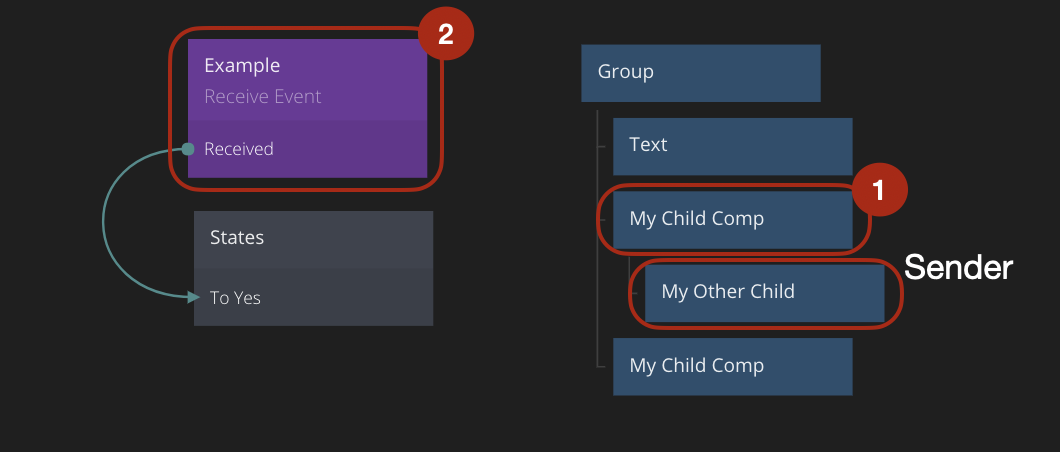
The final thing to know about propagation is the Consume property of the Receive Event node. If that property is checked it means that when that particular node receives an event it will stop the propagation. So no other Receive Event nodes after that one will receive this specific event.